Technically speaking, filtration is the act of removing suspended solids from a liquid by forcing the latter to move through the pores of a filter (a membrane with pores). Therefore, equipment used to filter, thicken, or clarify (to trap and remove insoluble matter from a liquid) a mixture of various materials is referred to as filtration equipment. Read More…
Our company is the filtering systems expert. We know everything there is to know about filtering liquids and oils for many industries ranging from the petrochemical industry to waste water management. It is our goal to provide customized solutions that you can trust and rely on every day. You will find that our attention to detail and superior service can help you in multiple ways. Contact us to...

At Dynamic Air Inc., we specialize in providing advanced filtration systems designed to meet the diverse needs of industries worldwide. Our team is committed to delivering high-performance products that ensure air quality and system efficiency. We design and manufacture a wide range of filtration solutions, including air filters, dust collectors, and ventilation equipment, tailored to enhance...

At Camfil APC, we are driven by a commitment to cleaner air and a healthier environment through the design and manufacture of advanced industrial filtration systems. As a global leader in air pollution control, we specialize in developing dust, mist, and fume collection solutions that protect workers, improve manufacturing efficiency, and ensure regulatory compliance.

At All American Air Filters, we take pride in delivering high-performance filtration solutions that protect air quality, extend equipment life, and support healthier environments across industrial, commercial, and institutional settings. Our expertise spans the design and manufacture of advanced air filtration systems engineered to capture contaminants, control particulates, and maintain optimal...
At Freudenberg Filtration Technologies, we dedicate ourselves to advancing air and liquid filtration systems that safeguard people, processes, and the planet. We combine decades of expertise with continual innovation to create solutions that enhance air quality, improve operational efficiency, and protect valuable assets.

More Filtration Equipment Manufacturers
How Filtration Equipment Works
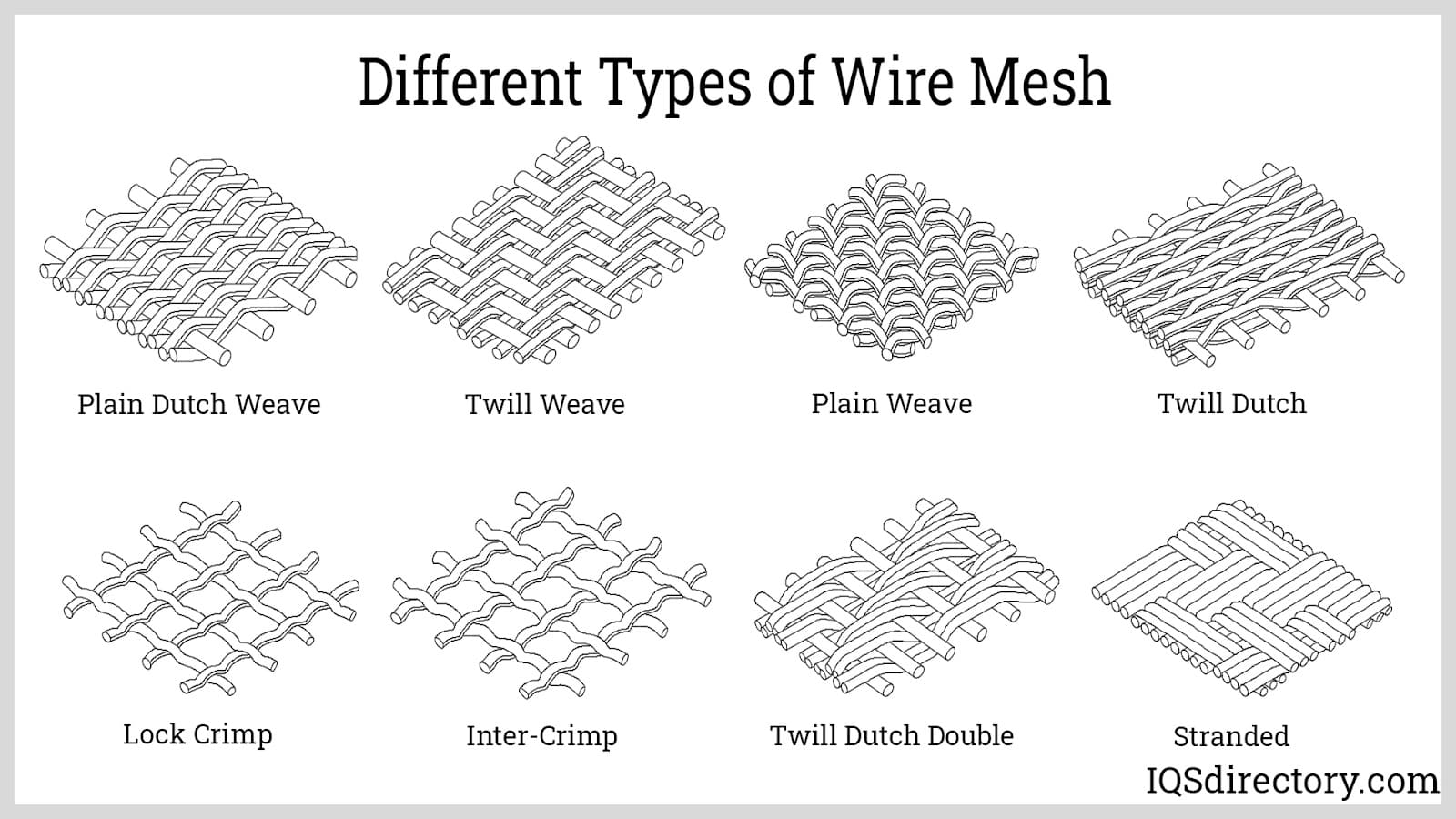
Filtration equipment plays a vital role in industrial processes, water treatment, environmental remediation, and countless other applications where separation of solids from liquids or gases is required. At its core, a filtration system utilizes a membranous screen or filter media with microscopic pores—these pores are engineered to allow only particles of a certain size (typically liquids or gases) to pass through, while physically blocking larger contaminants such as suspended solids, bacteria, and other harmful microorganisms.
Advanced filtration systems offer precision by tailoring pore size and filter media composition to target specific contaminants, ranging from sand and silt to pathogens like bacteria and viruses. If a filter's pores are sufficiently small, it can even remove microscopic organisms, making the resulting filtrate suitable for high-purity applications such as pharmaceutical manufacturing, food and beverage processing, and potable water production.

Understanding the principles behind filtration equipment is essential for selecting the right solution for your process, whether you are seeking removal of particulates from industrial wastewater, clarifying municipal drinking water, or achieving sterile filtration in laboratory environments.
Types of Filtration Equipment: An Overview of Technologies and Applications
Choosing the optimal filtration equipment depends not only on the nature of the contaminants but also on required flow rates, operating pressures, maintenance requirements, and compliance with industry standards. Below, we explore the major types of filtration equipment, their mechanisms, and common use cases:
Gravity Filtration Equipment
Gravity filtration is among the simplest and most cost-effective filtration methods. In gravity filtration equipment, the movement of liquid through the filter media is driven by hydrostatic pressure—the pressure exerted by a column of fluid above the filter surface. This passive process is favored for applications where gentle filtration is sufficient and energy consumption must be minimized.
- Sand Filters: Sand filters are the most widely used gravity filters. They consist of a tank filled with multiple layers of filter media, such as gravel, sand, or crushed anthracite. As water percolates downward, the filter bed traps suspended solids and particulates, forming a "filter cake" on the surface. Sand filtration is extensively used in municipal water treatment plants, swimming pool filtration, and industrial pre-filtration systems to remove turbidity and sediment.
- Bag Filters: Bag filters utilize a flexible felt or woven fabric formed into a bag-like structure. These filters are inserted into a housing, and liquid passes through the bag, which captures suspended solids. While bag filters are simple and economical, they are typically reserved for processes with low contaminant loads or where only coarse filtration is required. Common applications include pre-filtration in chemical processing, paint filtration, and coolant filtration in metalworking industries.
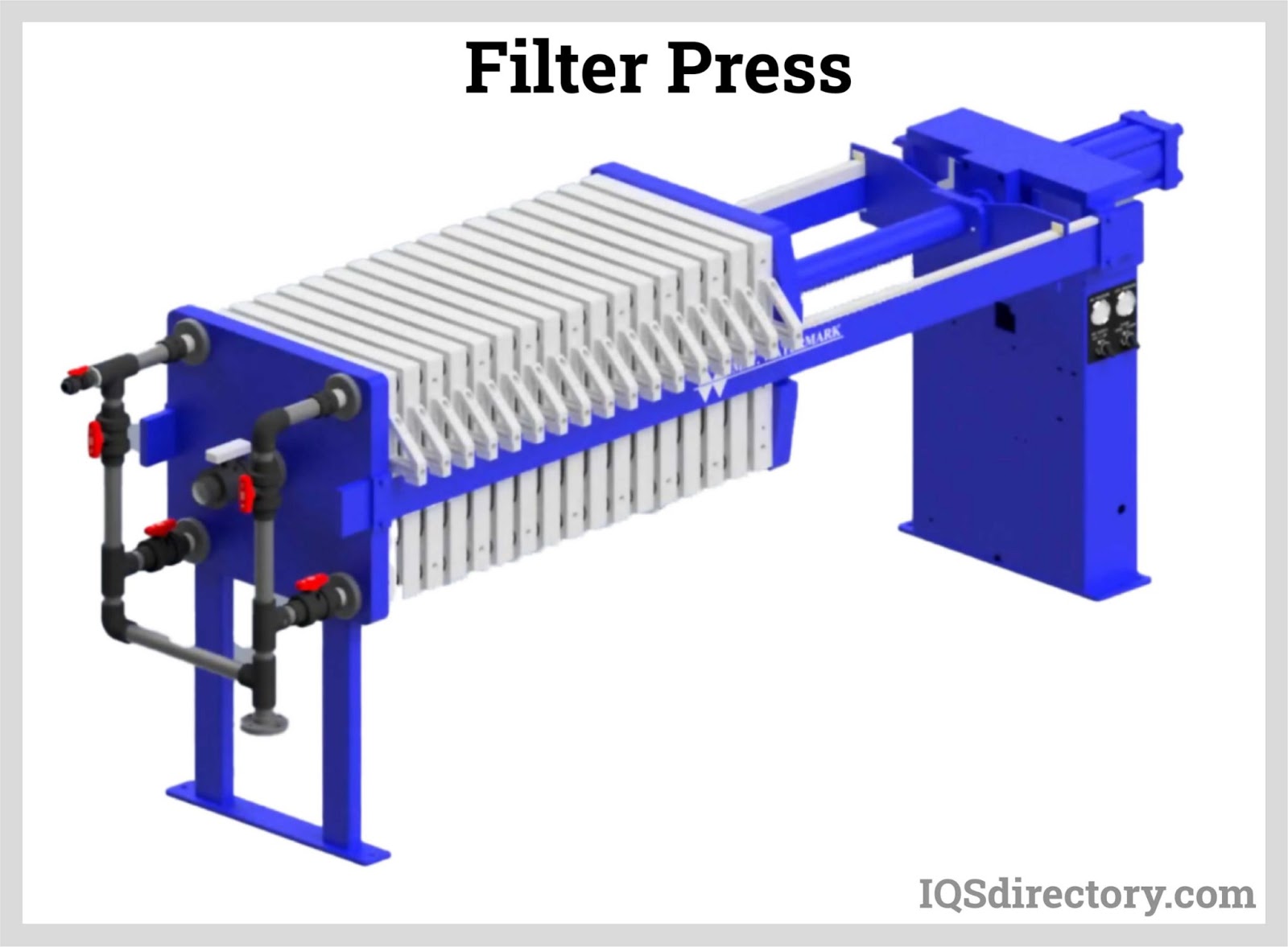
- Gravity Nutsche Filters: Gravity nutsche filters are closed vessels with a permeable, porous bottom for filtration. While traditionally operating under gravity, modern versions may incorporate pressure or vacuum assistance to increase throughput. Nutsche filters are favored in pharmaceutical and fine chemical manufacturing for batch filtration, especially where containment and product recovery are critical.

When should you choose gravity filtration equipment?
Gravity filtration is ideal for low-pressure applications, pre-treatment stages, and situations where energy efficiency and ease of maintenance are priorities. It is also suitable for removing large particles or initial clarification before further treatment.
Clarifying Equipment: Achieving High Purity and Clarity
Clarifying equipment is designed to separate fine suspended solids from liquids, producing a clear effluent. This category includes technologies such as suction clarifiers and reverse osmosis (RO) clarifiers, each suited to different contamination profiles and volume requirements.
- Suction Clarifiers: Suction clarifiers work on the principle of gravity settling. Heavier particulates gradually sink to the bottom of the tank, where they are collected and removed, often with the aid of scraper blades or suction arms. To enhance removal efficiency, flocculants or coagulants may be added to aggregate smaller particles into larger masses. Suction clarifiers are a mainstay in municipal and industrial wastewater treatment, sludge thickening, and mining operations.
- Reverse Osmosis (RO) Systems: Reverse osmosis is a high-efficiency water purification method that employs a semipermeable membrane to remove dissolved salts, organic molecules, bacteria, viruses, and other contaminants. Under pressure, water molecules are forced through the membrane, leaving impurities behind. RO systems are indispensable for producing ultrapure water in electronics manufacturing, food and beverage processing, and desalination of seawater for municipal supply.

What are the benefits of clarifying equipment?
Clarifying equipment delivers high clarity, consistent water or liquid quality, and reliable removal of fine particles and dissolved contaminants. This is essential for meeting regulatory standards, protecting downstream equipment, and ensuring product quality in industries from pharmaceuticals to food production.
Centrifugal Separators: Harnessing Centrifugal Force for Separation
Centrifugal separators employ the principle of centrifugal force to accelerate the separation of solids from liquids or liquids of differing densities. This technology offers rapid, continuous processing and is highly effective for challenging separations where gravity alone is insufficient.
- Centrifuges: A centrifuge spins the liquid-solid mixture at high speeds, causing denser particles to migrate outward and settle, while lighter phases remain closer to the axis. Centrifuges are available in various designs, including batch and continuous types, and are widely used in bioprocessing, dairy production, oil refining, and laboratory sample preparation.
- Hydrocyclones: Hydrocyclones utilize a tangential inlet to create a swirling motion, generating centrifugal forces that separate particles based on size, shape, and density. Hydrocyclones are valued in mineral processing, sand and gravel operations, and industrial wastewater treatment for their simplicity and high throughput.

Why use centrifugal separation?
Centrifugal separators provide rapid, automated removal of solids with minimal operator intervention. They are particularly useful for high-volume continuous processing and for separating emulsions or fine particulates that are difficult to remove by filtration or gravity settling alone.
Sedimentation Equipment: Gravity and Flocculation in Action
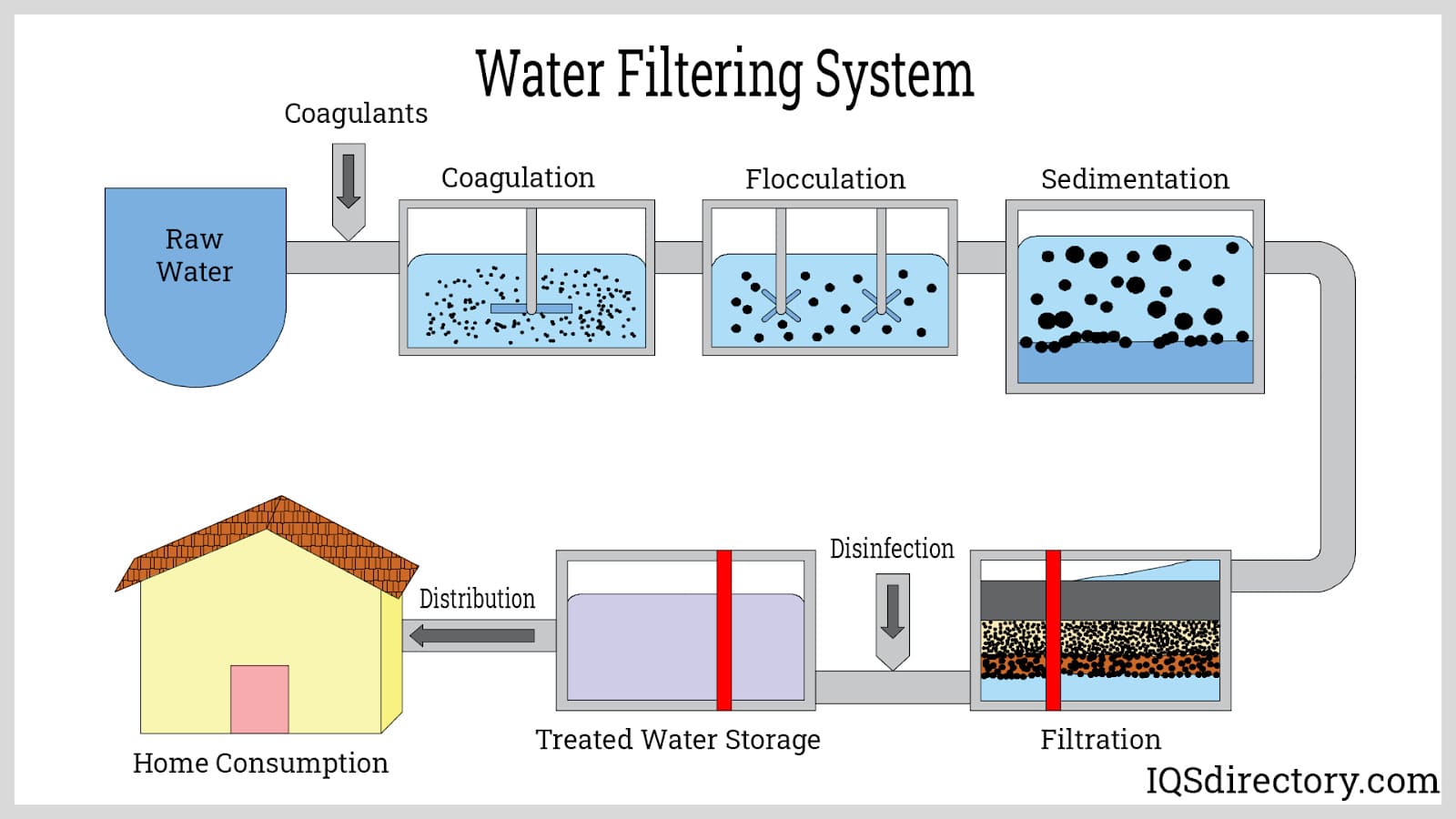
Sedimentation equipment capitalizes on the natural tendency of heavier particles to sink under gravity or to aggregate via chemical reactions (flocculation). This process is fundamental in water and wastewater treatment, mining, and process industries where bulk removal of solids is required.
- Gravity Sedimentation: In gravity sedimentation, denser solids settle to the bottom of a clarifier or settling tank, leaving clarified liquid above. The rate of settling is influenced by particle size, density, and fluid viscosity. Gravity sedimentation is commonly used as a primary treatment step in municipal water plants and industrial effluent treatment.
- Flocculation: Flocculation enhances sedimentation by using chemicals (flocculants) to bind small particles into larger aggregates (flocs), which settle more readily. Some systems may utilize magnetic fields to collect iron-containing particles or employ mechanical stirring to optimize floc formation. Flocculation is critical for removing fine colloidal particles, heavy metals, and pathogens from water and wastewater streams.

Looking for effective sedimentation equipment?
Consider sedimentation when you need bulk removal of suspended solids, especially as a cost-effective pre-treatment before finer filtration or advanced treatment methods.
Vacuum Filtration Equipment: Maximizing Throughput and Efficiency
Vacuum filtration equipment accelerates the separation of solids from liquids by applying a vacuum below the filter media, creating a pressure differential that draws liquid through more rapidly than gravity alone. This method is widely used in industrial processing, chemical manufacturing, and laboratories needing quick, efficient filtration.
- Batch Vacuum Filters: These include vacuum nutsche and vacuum leaf filters, which are descendants of gravity filters but incorporate vacuum pumps to enhance flow rates. Nutsche filters are prized in pharmaceutical and chemical industries for their closed, contained operation, making them suitable for hazardous or sensitive materials. Vacuum leaf filters, on the other hand, dip a large surface area filter into the slurry and use vacuum suction to draw the filtrate through, accumulating cake on the filter surface.
- Continuous Vacuum Filters: The rotary drum filter is the quintessential continuous vacuum filter. The drum rotates through a bath of slurry, and vacuum pressure draws liquid through the drum’s filter surface, leaving a cake of solids. This system is engineered for high-volume, continuous operations such as mineral processing, pulp and paper manufacturing, and wastewater treatment.
What are the advantages of vacuum filtration systems?
Vacuum filtration offers high throughput, efficient cake washing, and suitability for hazardous or corrosive environments. It is preferred where process speed, automation, and product purity are essential decision factors.
Advanced Filtration Methods and Emerging Technologies
As regulations and quality standards evolve, so too does filtration technology. Modern filtration equipment incorporates advanced materials and smart controls to improve performance, sustainability, and cost-effectiveness. Key innovations include:
- Membrane Filtration: Including microfiltration, ultrafiltration, nanofiltration, and reverse osmosis, these membrane systems use synthetic or polymeric membranes to achieve precise particle size cutoffs, making them essential for potable water production, biopharmaceuticals, and food processing.
- Self-Cleaning and Automated Backwash Filters: These systems reduce manual maintenance by automatically removing accumulated solids from the filter surface, ensuring continuous operation and reducing downtime in critical processes.
- Activated Carbon Filters: Often used as a polishing step, activated carbon adsorption removes chlorine, organic compounds, and trace contaminants from water and air streams, enhancing taste, odor, and safety.
- Electrostatic and Magnetic Filtration: These advanced methods capture fine particulates, metallic contaminants, or aerosols from air or fluid streams in electronics manufacturing, power generation, and specialty chemical processing.
How do you select the best filtration technology for your needs?
Considerations include the nature and concentration of contaminants, flow rate requirements, regulatory compliance, energy consumption, maintenance needs, and total cost of ownership. For complex requirements, a combination of filtration stages may be necessary, such as sedimentation followed by membrane filtration and carbon polishing.
Key Benefits of Modern Filtration Equipment
Investing in the right filtration equipment delivers significant operational, financial, and environmental benefits:
- Improved Product Quality: Consistent removal of contaminants ensures high standards in food, beverage, pharmaceutical, and chemical production.
- Equipment Protection: Filtration prevents abrasive or corrosive solids from damaging pumps, valves, heat exchangers, and other downstream assets.
- Regulatory Compliance: Advanced filtration systems help meet increasingly stringent water, air, and process effluent regulations, reducing the risk of fines or shutdowns.
- Reduced Operating Costs: Efficient filtration minimizes waste, optimizes chemical usage, and lowers maintenance and energy costs over the equipment lifecycle.
- Environmental Stewardship: By enabling recycling and reuse of process fluids and minimizing pollutant discharge, filtration supports sustainability goals and responsible resource management.
Common Applications and Industries Served
Filtration equipment is indispensable across a broad spectrum of industries and applications, including but not limited to:
- Municipal water treatment and desalination
- Industrial wastewater management and recycling
- Chemical and petrochemical manufacturing
- Pharmaceutical and biotechnology processing
- Food and beverage production (including brewing, dairy, and juice)
- Mining and mineral processing
- Oil and gas refining
- HVAC and air purification systems
- Power generation (boiler feedwater treatment)
- Laboratory and pilot plant operations
Which filtration equipment is best for your industry?
Use our filtering system directory to explore solutions tailored to your sector, or contact our experts for a customized recommendation based on your unique process and compliance requirements.
Decision Factors: How to Choose the Right Filtration Equipment Supplier
Choosing the right filtration equipment supplier is as critical as selecting the equipment itself. Consider the following factors during your evaluation:
- Technical Expertise & Experience: Does the supplier have a proven track record with your industry’s specific filtration challenges?
- Product Range & Customization: Can they provide standard and custom filtration systems to fit your application and process parameters?
- After-Sales Support & Service: Do they offer comprehensive installation, maintenance, and troubleshooting support to maximize uptime?
- Certifications & Regulatory Compliance: Are their products certified to meet local and international safety, quality, and environmental standards?
- Cost of Ownership: Are pricing, maintenance, and consumable replacement costs competitive?
- Innovation & Technology: Are they up-to-date with the latest filtration technologies, including automation, remote monitoring, and energy efficiency features?
To ensure you achieve the best results when purchasing filtration equipment, compare several companies using our directory of filtration equipment suppliers. Each supplier has a business profile page highlighting their areas of experience and capabilities, along with a contact form for direct communication or to request a quote. Review each business website using our proprietary website previewer for a quick overview of their specialties. Then, use our simple RFQ form to contact multiple filtration equipment companies with a single inquiry.
Ready to start your search for the ideal filtration solution?
Visit our filtration equipment directory to browse industry-leading suppliers, compare filtration technologies, and request tailored quotes for your specific project needs.
Frequently Asked Questions About Filtration Equipment
- What types of contaminants can filtration equipment remove? Filtration systems can remove suspended solids, bacteria, viruses, dissolved salts, organic compounds, heavy metals, oils, and more, depending on the technology and filter media used.
- How do I determine the right filter pore size for my application? Filter pore size selection depends on the smallest contaminant you need to remove. For example, bacteria are typically 0.2-2 microns, so a 0.2-micron filter is required for sterilization, while sand and silt can be removed with much larger pores.
- What are the maintenance requirements for filtration equipment? Maintenance varies by type—some filters require regular media replacement or cleaning, while others, like self-cleaning filters, automate this process. Always follow manufacturer recommendations for optimal performance and longevity.
- Can filtration systems be automated? Yes, many modern filtration systems offer automation features for monitoring performance, scheduling maintenance, and integrating with plant control systems to maximize efficiency and minimize downtime.
- What is the difference between filtration and separation? Filtration specifically refers to passing a fluid through a porous medium to remove solids, while separation is a broader term encompassing other methods such as centrifugation, sedimentation, and flotation.
Take the Next Step: Connect with Top Filtration Equipment Suppliers
Whether you need a turnkey water treatment solution, custom industrial filtration system, or laboratory-scale filter setup, finding the right partner is critical for achieving operational efficiency and regulatory compliance. At Filtering Systems, we connect you with trusted filtration equipment manufacturers and service providers who offer:
- Comprehensive product lines covering gravity, vacuum, centrifugal, membrane, and specialty filtration technologies
- Custom engineering and process integration support
- Expert technical consultation and application-specific guidance
- Rapid quotes and responsive customer service
- Ongoing maintenance, spare parts, and system optimization services
Browse our filtration equipment supplier directory or get in touch with our team for personalized assistance. Compare options, request a quote, and make an informed decision for your next filtration project.
Still have questions about filtration equipment? Contact us today for expert advice, product recommendations, or to discuss your filtration challenges and requirements. Our knowledgeable team is ready to help you achieve the best filtration performance for your application.
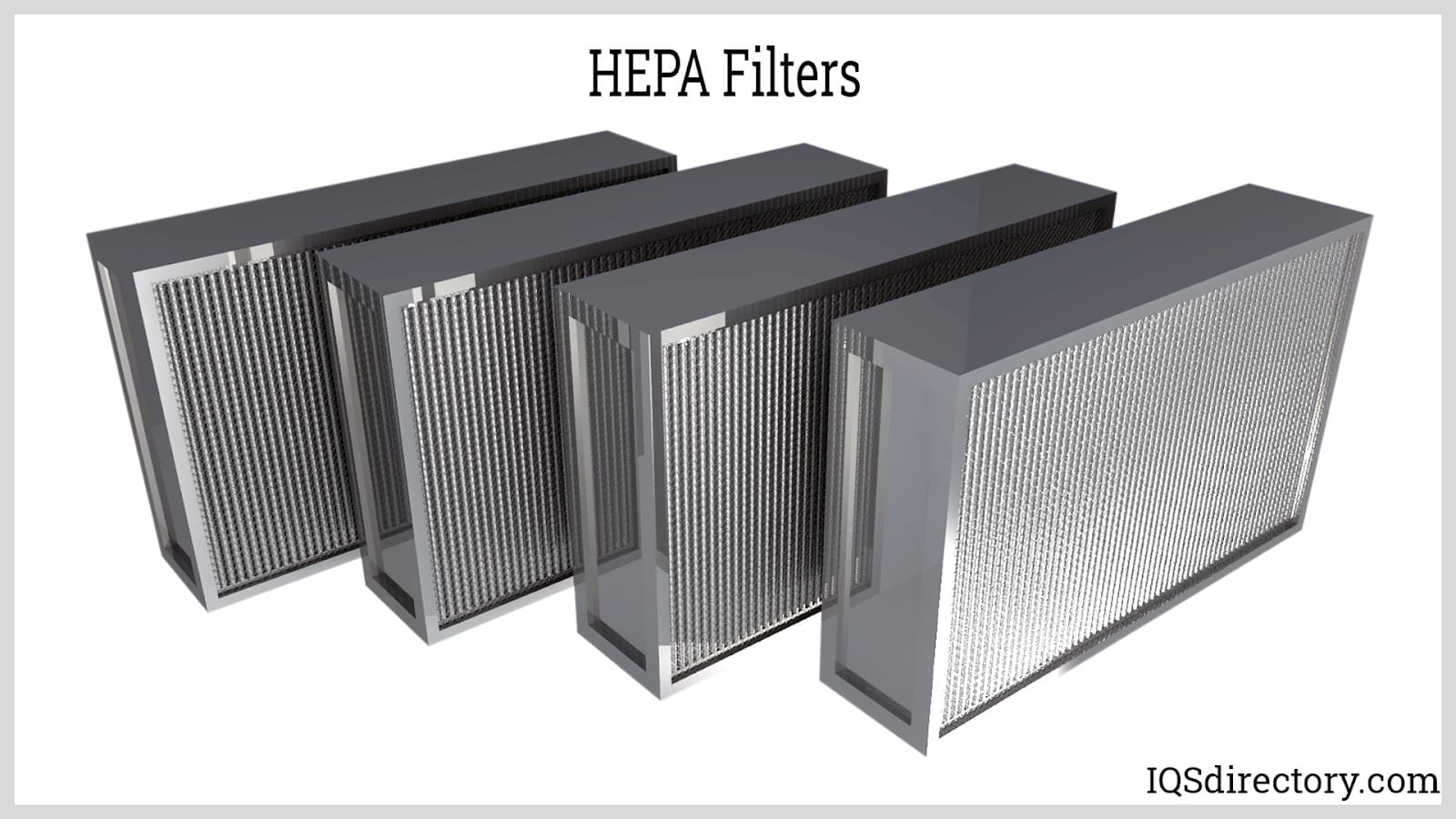





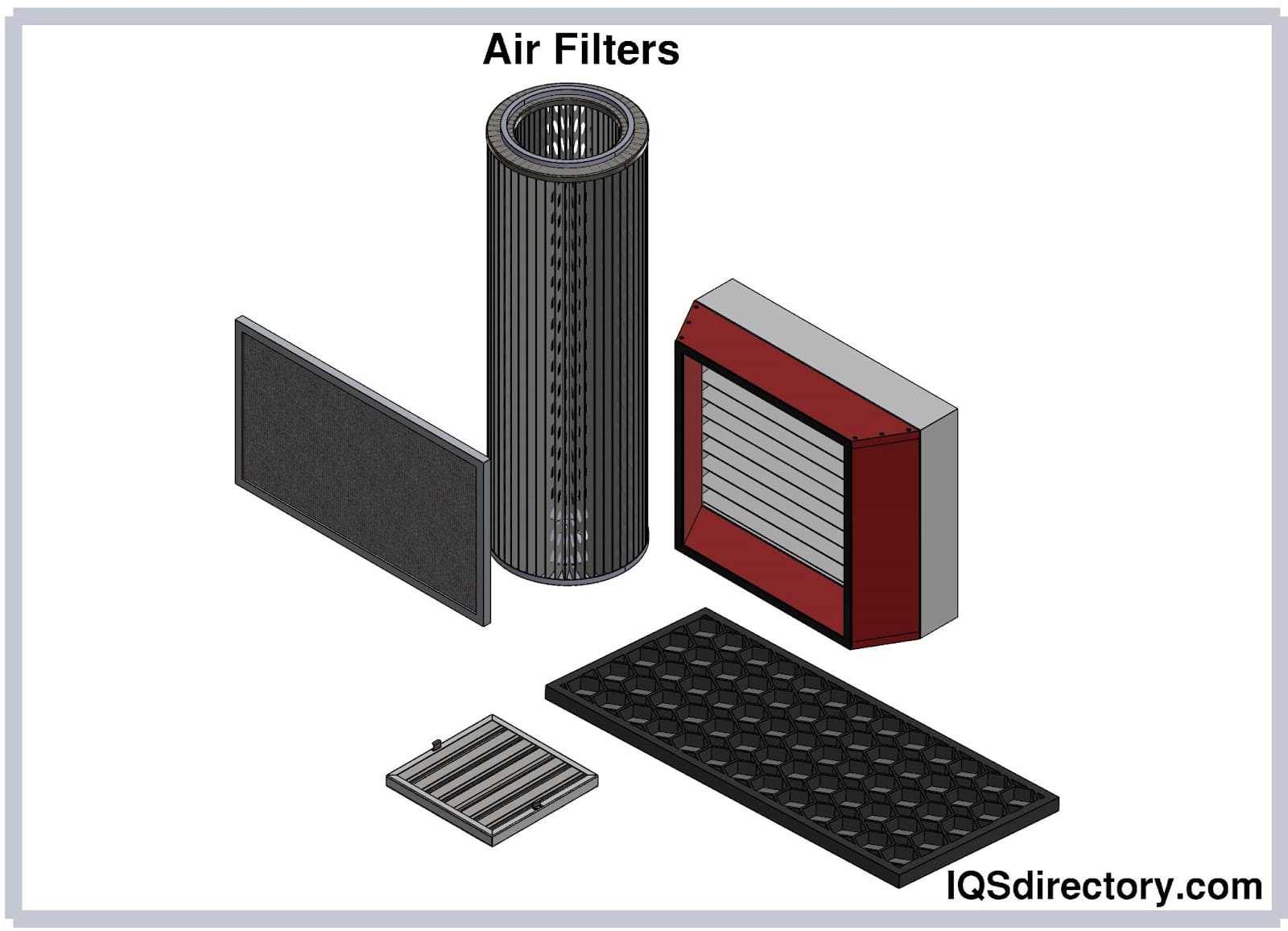

 Air Filters
Air Filters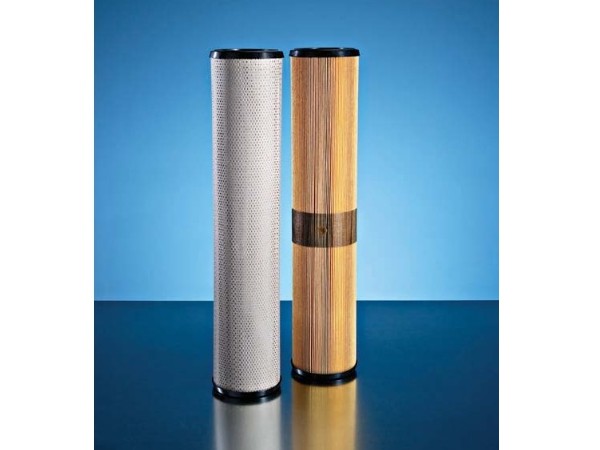 Liquid Filters
Liquid Filters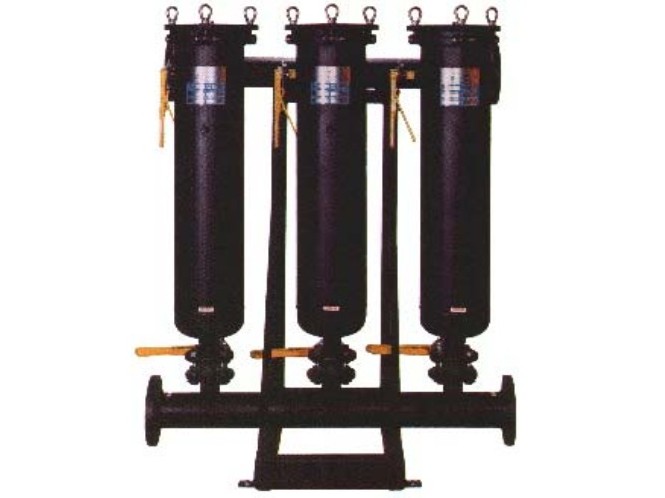 Filtering Systems
Filtering Systems Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services