Filtration systems are used to process, separate, or clarify a stream by separating elements and removing debris. The goal of a filtration system is to cause the air or fluid being processed to be as pure as possible. Filtration systems help keep the environment safer for people and buildings both where fluids are being processed in the surrounding areas. Read More…
Our company is the filtering systems expert. We know everything there is to know about filtering liquids and oils for many industries ranging from the petrochemical industry to waste water management. It is our goal to provide customized solutions that you can trust and rely on every day. You will find that our attention to detail and superior service can help you in multiple ways. Contact us to...

At Dynamic Air Inc., we specialize in providing advanced filtration systems designed to meet the diverse needs of industries worldwide. Our team is committed to delivering high-performance products that ensure air quality and system efficiency. We design and manufacture a wide range of filtration solutions, including air filters, dust collectors, and ventilation equipment, tailored to enhance...

At Camfil APC, we are driven by a commitment to cleaner air and a healthier environment through the design and manufacture of advanced industrial filtration systems. As a global leader in air pollution control, we specialize in developing dust, mist, and fume collection solutions that protect workers, improve manufacturing efficiency, and ensure regulatory compliance.

At All American Air Filters, we take pride in delivering high-performance filtration solutions that protect air quality, extend equipment life, and support healthier environments across industrial, commercial, and institutional settings. Our expertise spans the design and manufacture of advanced air filtration systems engineered to capture contaminants, control particulates, and maintain optimal...
At Freudenberg Filtration Technologies, we dedicate ourselves to advancing air and liquid filtration systems that safeguard people, processes, and the planet. We combine decades of expertise with continual innovation to create solutions that enhance air quality, improve operational efficiency, and protect valuable assets.

More Filtration System Manufacturers
In modern industrial operations and machinery, filtration systems are essential for maintaining clean, efficient, and consistent performance. Industrial filters play a crucial role in processing a variety of fluids—such as gasoline, oil, diesel, hydraulic fluid, water, and exhaust air—ensuring these substances meet stringent industry-specific standards and regulatory requirements. Whether you operate in manufacturing, power generation, or chemical processing, implementing the right filtration technology protects your equipment, improves product quality, and reduces downtime caused by contamination.
Our advanced air filtration systems and water filtration solutions are trusted across a wide spectrum of industries. These include food processing, automotive engineering, mining, chemical engineering, municipal water treatment, and environmental health services. Beyond industrial applications, our reliable filtration systems also fulfill commercial and residential needs, helping homeowners and businesses maintain healthy air and water quality.
History of Filtering Systems
The history of filtering systems stretches back thousands of years, with roots in ancient civilizations such as Egypt and India. Archaeological discoveries in the tombs of Ramses II and Amenophis II reveal the Egyptians’ use of sand filters to purify drinking water—sand’s natural properties helped capture and settle suspended particles, producing clearer water for daily use and ceremonial purposes. Ancient Indian texts, like the Sushruta Samhita, describe water purification methods including sun-heating, boiling, and filtration through gravel, showcasing early innovations in water treatment.
In ancient Greece, around 500 BC, the physician Hippocrates made a significant contribution to filtration technology by inventing the first bag filter, known as the Hippocratic Sleeve. By pouring boiled water through a cloth bag, he successfully removed sediments, improving both the taste and the safety of water for medical baths. This innovation marked an early form of medical water filtration that would influence later developments in public health.
From antiquity through the Middle Ages, filtration technology in Europe evolved slowly. Notably, in the 8th century, Arabian alchemist Gerber revolutionized water purification by inventing purification stills linked with wick siphons, which enabled water to be purified as it transferred between chambers. These advances influenced both scientific inquiry and public health practices for centuries.
The Renaissance and subsequent centuries saw renewed scientific interest and developments in filtration. In the 1500s, early forms of air filtration systems—primitive respirators—were developed to improve worker safety. In 1627, Sir Francis Bacon experimented with desalination processes using sand. Although his methods were not immediately successful, they spurred further research into water purification and contaminant removal.
By the late 17th century, the invention of the microscope by Robert Hooke and Antonie van Leeuwenhoek allowed scientists to observe microscopic pathogens in water, highlighting the necessity of effective water filtration. This discovery laid the foundation for the germ theory of disease and drove innovation in water treatment technologies.
The concept of reverse osmosis was first observed in 1748 by Jean-Antoine Nollet, but practical applications in filtration did not emerge until the 20th century, when materials science made it possible to manufacture fine-pored membranes for industrial use.
The 19th century brought major advances: in 1804, John Gibb of Paisley, Scotland, introduced sand filtration for municipal water purification. Around this time, ceramic filters gained popularity, and by 1830, London had established its first water treatment plant, ushering in the era of centralized water purification.
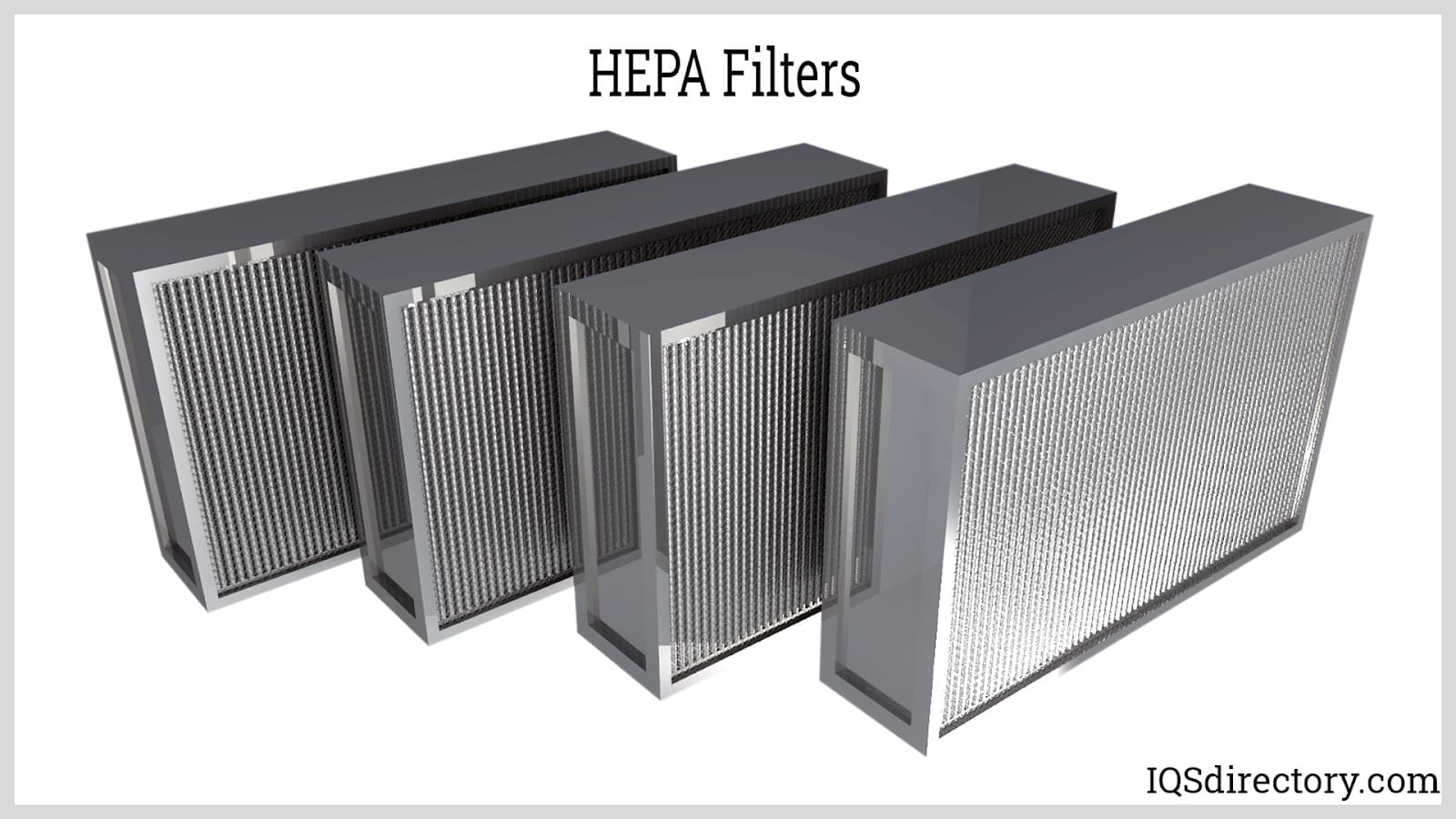
Air filtration technology also advanced dramatically in the 20th century. During World War II, the U.S. Army Chemical Corps and the Atomic Energy Commission developed the HEPA filter (High Efficiency Particulate Air filter) to protect scientists from radiation exposure during the Manhattan Project. After the war, the technology was released for public use, quickly becoming a standard in industrial, commercial, and residential filtration applications.
Ongoing improvements in filter media—ranging from cellulose and synthetic fibers to advanced ceramics and membranes—have further increased filtration efficiency. The environmental movement of the 1970s, regulatory measures like the U.S. Clean Water Act of 1972, and growing concerns about air pollution have made effective air and water filtration even more critical for compliance and public health. Today, advanced filtration systems are indispensable in fields such as aerospace, pharmaceuticals, electronics manufacturing, and healthcare.
How Filtering Systems Work
Modern filtration systems employ a variety of mechanisms to separate contaminants from liquids or gases. Some systems use mechanical filtration by trapping particles within a porous medium. Others rely on membrane filtration, where a semi-permeable membrane selectively allows certain molecules to pass while blocking contaminants. Additional techniques include foam filtration for capturing oil and grease, centrifugal filtration for separating solids via rotational force, gravity filtration for simple particle removal, and electrostatic filtration for attracting and collecting charged particles. In certain cases, biological agents are employed, particularly in wastewater treatment, to break down organic pollutants.
Some advanced filtration technologies also utilize hydrostatic or rotational pressure to enhance separation efficiency, particularly in high-volume or high-contaminant environments. Understanding the operating principle behind each system is vital when selecting the best solution for your application.
Types of Filtering Systems
Choosing the right filtration technology depends on your application, contaminant type, and operational requirements. Below, we outline the most common types of filtration systems used in industry, commerce, and residential settings:
- Vacuum filters: These systems create a lower pressure at the filter media outlet, drawing external air or fluid through the filter. Common in food processing, chemical manufacturing, and laboratory environments, vacuum filtration ensures rapid and efficient contaminant removal.
- Pressure filters: By using pressurized fluids or compressed air, these filters force liquids through filter media, effectively separating suspended solids and other impurities. Pressure filtration is widely used in hydraulic systems, oil processing, and beverage production.
- Membrane filtration: Utilizing thin, semi-permeable sheets, these systems excel at separating contaminants from liquids at the molecular level. Membrane filters are crucial for water purification, pharmaceuticals, and semiconductor manufacturing.
- In-line filters: Installed directly within pipelines or fluid circuits, in-line filtration systems capture debris, particulates, and contaminants before they can damage equipment or compromise product quality. Common in automotive, HVAC, and industrial process systems.
- Chemical filters: These filters use chemical adsorption to extract contaminants as fluids pass through. Activated carbon filters are a prime example, effectively removing chlorine, organic compounds, and odors from water and air.
- Biological filters: Employed mainly in wastewater treatment and aquaculture, biological filtration systems use beneficial microbes to break down organic pollutants.
- Electrodialysis systems (ED): These systems separate ions using membranes that permit only positively or negatively charged ions to pass, making them effective in desalination and water softening.
- Electrolysis reversal systems (EDR): Operating similarly to ED systems, EDR periodically reverses the electrical current to clean the membranes, maintaining high efficiency over time.
- Reverse osmosis (RO) systems: RO filtration uses high pressure to force water through a semi-permeable membrane, removing dissolved salts, bacteria, and other impurities. Ideal for residential drinking water, industrial process water, and desalination.
- Ultrafiltration (UF) filters: Designed to capture extremely small particles, viruses, and bacteria (down to 0.003 micrometers), UF systems are popular in biotechnology, pharmaceuticals, and potable water treatment.
- Electrodeionization (EDI) filters: These combine membranes, resins, and electrical current to remove dissolved ions from water, producing ultra-pure water for laboratory, electronics, and medical applications.
- Progression filtration systems: These systems use multiple stages or media to progressively capture different sizes of contaminants, ensuring high purity and efficient contaminant recovery. Common in mining and metalworking.
- Oil filtration systems: Specialized systems for removing particulates and water from engine, hydraulic, and transmission oils. They extend equipment life and reduce maintenance costs. For more details, see our dedicated oil filtration systems page.
- Coalescing filters: Designed to separate and remove mists, vapors, and oil aerosols from compressed air and gas streams, coalescing filters protect sensitive equipment and improve air quality. Learn more about coalescing filter manufacturers.
- Water filters: Essential for purifying tap water, drinking water, and wastewater by eliminating bacteria, viruses, heavy metals, and particulates. Also widely used as refrigerator water filters and for ice production.
- Pool filters: Purpose-built for maintaining clean, safe pool water. Most pool filtration systems use removable cartridges or sand filters for effective debris removal.
- HEPA filters: High Efficiency Particulate Air (HEPA) filters remove at least 99.97% of airborne particles as small as 0.3 microns. They are mandatory in clean rooms, aircraft cabins, hospitals, and high-end vacuum cleaners. See our filtration equipment section for more details.
- Magnetic filtration systems: These use strong magnets to remove ferrous particles (e.g., metal shavings and debris) from fluids. Magnetic separation is vital in food processing, oil and gas, pharmaceuticals, and water treatment for quality control and equipment protection.
Are you unsure which filtration system is right for your application? Contact us to discuss your industry requirements, contaminant concerns, and system performance goals.
Advantages and Benefits of Magnetic Filtration Systems
Reusable Technology and Reduced Costs
Magnetic filtration systems offer a highly cost-effective solution for particle removal, especially when compared to disposable filters. Once installed, magnetic filters require minimal ongoing investment, as there are no recurring expenses for filter replacements. This makes them ideal for high-volume industrial processes, reducing both operational costs and environmental impact.
Improved Fluid Flow
Unlike traditional filters that can impede fluid flow as media becomes clogged, magnetic filters provide continuous contaminant removal without significant pressure drop. This ensures consistent fluid movement, prolonging equipment life and reducing the risk of costly downtime in systems relying on hydraulic oils, lubricants, or coolants.
Provides Support to Conventional Filters
Integrating magnetic filters with conventional filtration systems enhances contaminant capture while reducing the load on disposable filters. This synergy increases the overall filtration efficiency and can extend the lifespan of standard filters by two to three times, translating into lower maintenance costs and reduced waste generation.
Environmentally Friendly
Magnetic filtration is a sustainable approach to fluid purification. By eliminating much of the need for disposable filter media (such as paper cartridges), it significantly reduces landfill waste and hazardous material disposal. The ability to recycle captured ferrous particles further supports circular economy goals and corporate sustainability initiatives.
Improves Electro-Hydraulic Valves
Industrial operations that rely on electro-hydraulic systems benefit greatly from magnetic filtration. By removing abrasive particles that could cause valve sticking, wear, or failure, magnetic filters ensure optimal valve performance, reduce repair costs, and enhance overall safety.
Reduced Risk of Oil Oxidation
Contaminant metals accelerate oil oxidation, leading to sludge, rust, and corrosion inside engines and hydraulic systems. Magnetic filters continuously remove these metallic particles, improving oil quality, extending oil change intervals, and decreasing the need for hazardous waste disposal.
Better Gravity Flow
Gravity-fed systems often struggle with traditional filters due to limited pressure. Magnetic rods and plugs, however, extract ferrous contaminants with minimal flow restriction, making them ideal for applications where gravity is the primary driving force.
Want to know more about industrial magnetic filtration or to compare magnetic filters vs. disposable filters for your process? Request a consultation with our filtration experts today.
Filtering System Design and Customization
Effective filtration system design requires careful consideration of the application, contaminant type, flow rate, and environmental conditions. Manufacturers tailor filtration solutions based on:
- Type of fluid or gas: Is it water, oil, hydraulic fluid, air, or another medium?
- Contaminant characteristics: What particle sizes, chemical compositions, or biological loads must be removed?
- Operating environment: Will the system be installed in a factory, clean room, commercial kitchen, or residential household?
- Performance standards: Compliance with ISO, ASTM, ANSI, or industry-specific guidelines.
- Installation requirements: Do you need point-of-entry, inline, or exhaust-side filtration? Will multiple filtration stages improve system performance?
Manufacturers select filter pore sizes and media based on the size and nature of the targeted contaminants. The chosen filter media—be it activated carbon, Teflon, resin, nylon, sand, or synthetic fibers—must balance filtration efficiency with flow rate and maintenance needs. For example, carbon media is highly effective at removing chlorine and volatile organic compounds from water, while HEPA-grade synthetic fibers capture fine airborne particulates in clean rooms and healthcare facilities.
Filter housings and cartridges are typically constructed from robust materials such as aluminum, plastic, steel, or stainless steel to withstand harsh operating conditions, chemicals, or high temperatures. Customization may also involve designing filters for specific operating pressures, flow rates, or space constraints.
Not sure which filter design will best meet your industry requirements? Explore our filtering system customization options or contact us for expert guidance.
Filtering System Safety and Compliance Standards
Adhering to filtration safety standards ensures system reliability and regulatory compliance. Different applications demand conformity with various guidelines:
- ASTM, ANSI, ISO Technical Committee 131: Provide general and industry-specific filtration standards.
- Hospital and healthcare filtration: ANSI collaborates with the American Society for Healthcare Engineering to set standards for hospital air and water filtration systems.
- HEPA filters: Must meet stringent U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) and National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) requirements for particle removal efficiency.
- Food, beverage, and pharmaceutical filtration: Subject to FDA and NSF international standards for contaminant control and material safety.
- Municipal water treatment: Must comply with EPA regulations, such as the Safe Drinking Water Act.
Ensuring your filtration system meets relevant standards is critical for operational safety, environmental protection, and brand reputation. Consult with certified filtration experts to verify your compliance.
Choosing the Right Filtering System Manufacturer
Ready to select the best filtration system manufacturer for your needs? Follow these steps to streamline your search and ensure you find a partner capable of delivering quality, reliability, and value:
- Define your application: Specify the type of fluid or air to be filtered, the contaminants to be removed, and the system’s end use (e.g., industrial water treatment, HVAC air purification, food-grade oil filtration).
- Clarify requirements: Set your budget, project timeline, compliance and safety standards, desired flow rates, and space constraints.
- Consider lifecycle costs: Compare initial investment, ongoing maintenance, replacement filter availability, and total cost of ownership.
- Evaluate manufacturer support: Ask about technical support, installation services, custom engineering, and post-sale maintenance plans.
- Request case studies: Look for proven experience with your industry and application. Ask for references, certifications, and documented results.
Comparing these factors will help you eliminate unsuitable suppliers and focus on those best equipped to meet your needs. However, the sheer volume of manufacturers and filtration equipment providers online can be overwhelming. To help you get started, we’ve curated a list of top-rated filtration system manufacturers—see above to explore their profiles and learn more about their products and capabilities.
Frequently Asked Questions About Filtration Systems
- What type of filtration system is best for my industry?
This depends on your specific contaminants, operational environment, required flow rates, and regulatory standards. Contact our experts for a custom recommendation. - How often should industrial filters be replaced or serviced?
Service intervals vary by filter type, usage, and contaminant load. Many advanced filters feature monitoring systems to alert you when maintenance is due. - What is the difference between HEPA and ULPA filters?
Both are high-efficiency air filters; however, ULPA (Ultra Low Penetration Air) filters capture even smaller particles than HEPA, making them ideal for clean room and pharmaceutical applications. - Can filtration systems be customized for my process?
Yes, leading manufacturers offer custom filtration solutions tailored to your operational requirements, fluid types, and contaminant profiles. - How do I ensure my filtration system complies with regulations?
Work with manufacturers who provide certification, documentation, and ongoing support to guarantee adherence to applicable standards (EPA, FDA, ISO, etc.).
Take the Next Step in Filtration System Selection
Whether you need a new industrial filtration system, want to upgrade existing water or air filtration equipment, or are exploring advanced technologies like reverse osmosis or magnetic separation, partnering with the right manufacturer is critical. Assess your unique needs, compare solutions, and consult with industry experts to ensure the longevity, safety, and efficiency of your operations.
For more guidance, explore our in-depth resources on water filtering systems, oil filtration systems, and coalescing filter systems. Or, if you’re ready to connect with a qualified supplier, visit our filtration system manufacturer directory today.
Enhance your operational reliability, product quality, and environmental sustainability with the right filtration system—designed, engineered, and installed for your specific needs.


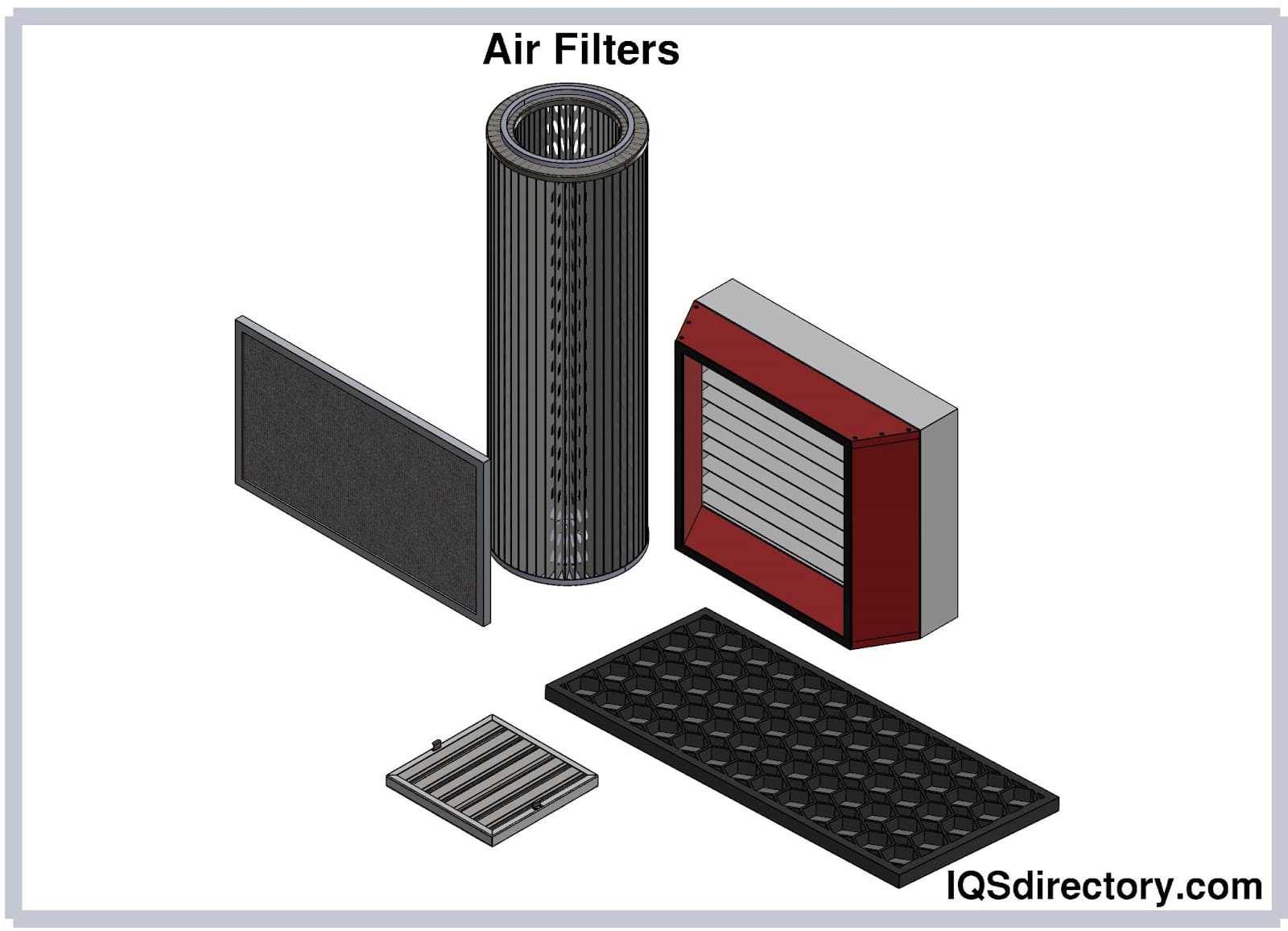

 Air Filters
Air Filters Liquid Filters
Liquid Filters Filtering Systems
Filtering Systems Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services